Why Sheet-Based Activated Carbon is Revolutionizing the Food & Beverage Industry
January, 2024
What is activated carbon?
Activated carbon is an effective method of removing undesirable contaminants across a wide range of food and beverage applications including purification, flavor removal and decolorization. Unlike bleaching processes, color removal occurs through a process called adsorption.
Adsorption is the uptake or physical binding of gases, vapor or particles dissolved or suspended in liquids to the surface of a solid porous material. Van der Waals force causes the carbon atoms on the surface of the activated carbon to attract molecules of gases and liquids. Depending on the concentration of the material to be adsorbed, an equilibrium is formed between the phase (liquid, gas, or air) and the surface of the activated carbon.
However, there are challenges leveraging loose activated carbon in food and beverage filtration processes, and it often does not provide optimal efficiency of adsorption. Review the table below to learn more about loose/bulk powder activated carbon (PAC) and how sheet-based solutions may improve efficiencies and reduce costs.
Bulk Powdered Activated Carbon (PAC) Challenges | Advantages of Sheet-Based Activated Carbon Products |
|---|---|
| Handling and mixing of bulk PAC is labor intensive and requires capital expenditure for specialized equipment. | At an optimized flow rate, the probability of contact between impurities and carbon particles is greater in carbon-impregnated sheets making it low maintenance. This adsorption efficiency will reduce overall process time. Modules fit directly into enclosed housings. |
| Cleaning of process equipment after the product has been treated is labor intensive. | Sheet-based activated carbon products should improve and provide simplified handling and cleaning. |
| Removal of residual PAC from the treated product generally requires additional filtration steps which add cost to the overall process. | The sheet's depth (thickness) results in a series of layers containing PAC. The initial layers make first contact with the fluid and as time and increasing fluid volume is passed through this layer, they are the first to become saturated with impurity. Subsequent layers, however, still have adsorbing sites and a capacity to adsorb impurities. Therefore, the likelihood of adsorption increases through the depth of the media. In essence, having a depth of PAC and passing the fluid at an optimal flow rate through that depth enables the carbon to be fully utilized in adsorbing impurities. |
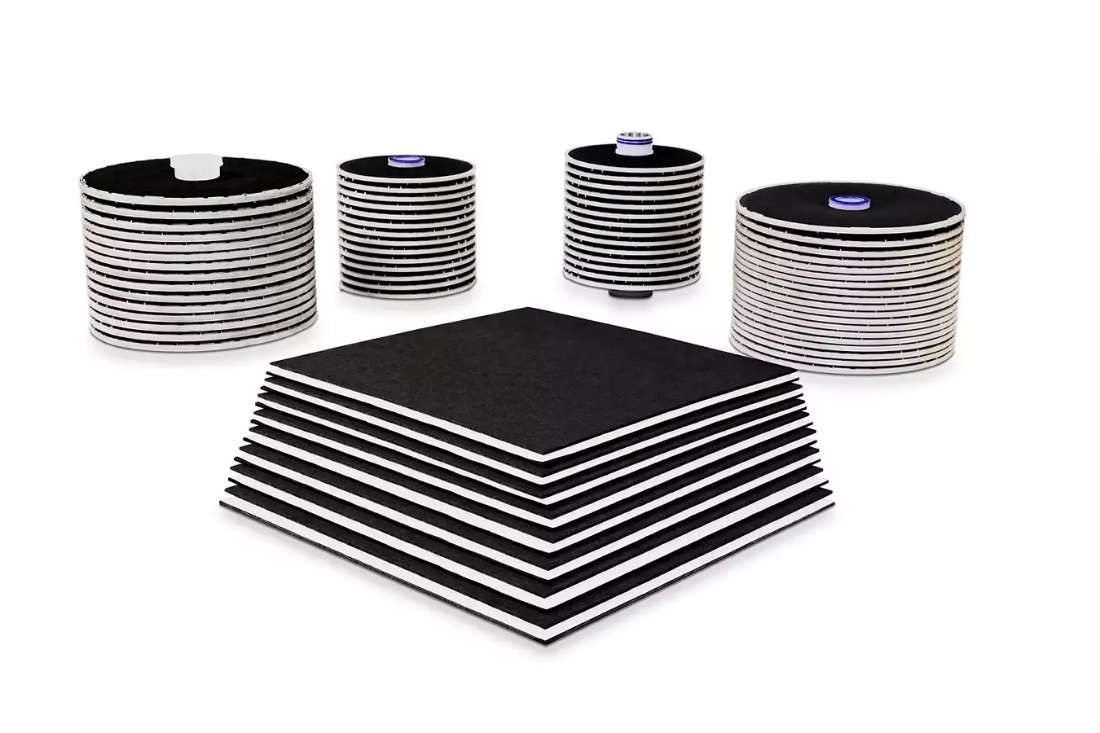
Pall solutions in activated carbon media
Pall’s AKS modules alleviate the PAC drawbacks with modules that fit directly into the enclosed housings to achieve color removal. During the adsorption process, AKS modules combined with Seitz® AKS media can remove or correct color and flavor. Explore our e-shop for more information.
What next?
After years of unparalleled expertise in supplying activated carbon media, Pall is now launching the next generation of activated carbon solutions that will cater exclusively to the food and beverage industry.
Discover more here
Subscribe to our blog to stay up-to-date on the latest food and beverage insights and trends
- Category
- Author
- Sort By