Reduce Clostridium Botulinum Contamination Risk
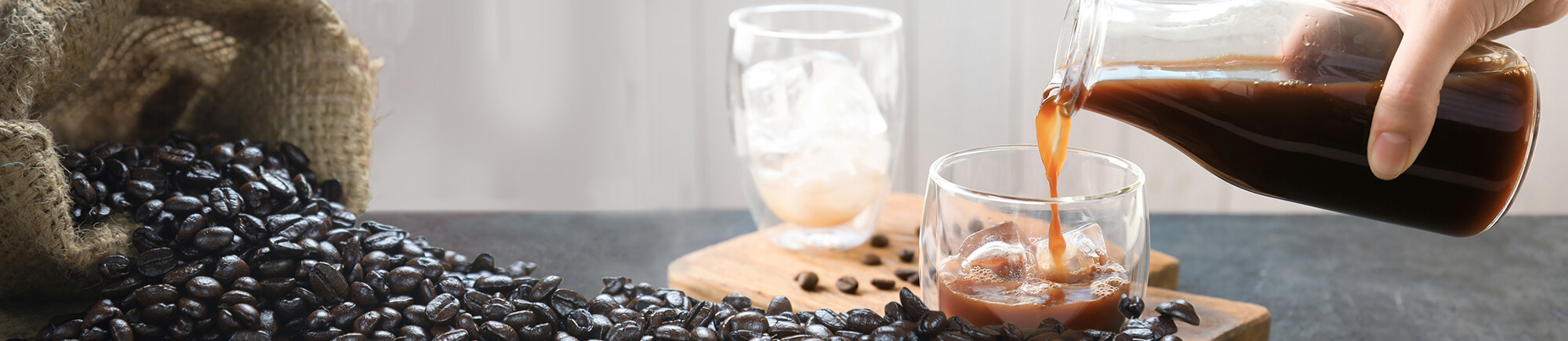
In recent years, consumption of cold brew coffee has exploded. The market rose to 21 percent in 2017 among those drinking coffee daily in the U.S., up from 15 percent in 2015, according to data from the New York-based National Coffee Association1.
With growing consumer awareness and a desire to consume refreshing RTD beverages, this trend is expected to continue. Cold brew coffee offers consumers a subtler, yet sweeter substitute to hot brewed coffee. The RTD beverage is produced using cool water which results in a lower extraction of oils yielding a sweeter taste. However, on the downside, the production cost of cold brew, including cold brew filtration processes, is significantly higher than traditional coffee given production requires more than double the volume of coffee grinds.
Ensuring Safety in Cold Brew Coffee Production
With rising consumption and broadening distribution, attention to product quality and safety has been increasing. As a low acid food with typical pH greater than 4.6 and a water activity greater than 0.852 , packaged cold brew coffee extract can potentially be a host for mold and harmful microorganisms such as Clostridium botulinum without proper processing. While Clostridium botulinum spores are generally harmless, the danger occurs when vegetative C. botulinum bacteria produce neurotoxins. The risk increases substantially in immunocompromised individuals.
Meeting FDA Guidelines for Cold Brew Coffee Processing
Regulatory agencies like the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) are now setting stricter standards for low acid food as a preventative measure. For example, all commercial processors of low-acid and acidified foods located in the United States and all processors in other countries who export low-acid canned food or acidified food products into the United States must register their processing plants with the FDA.
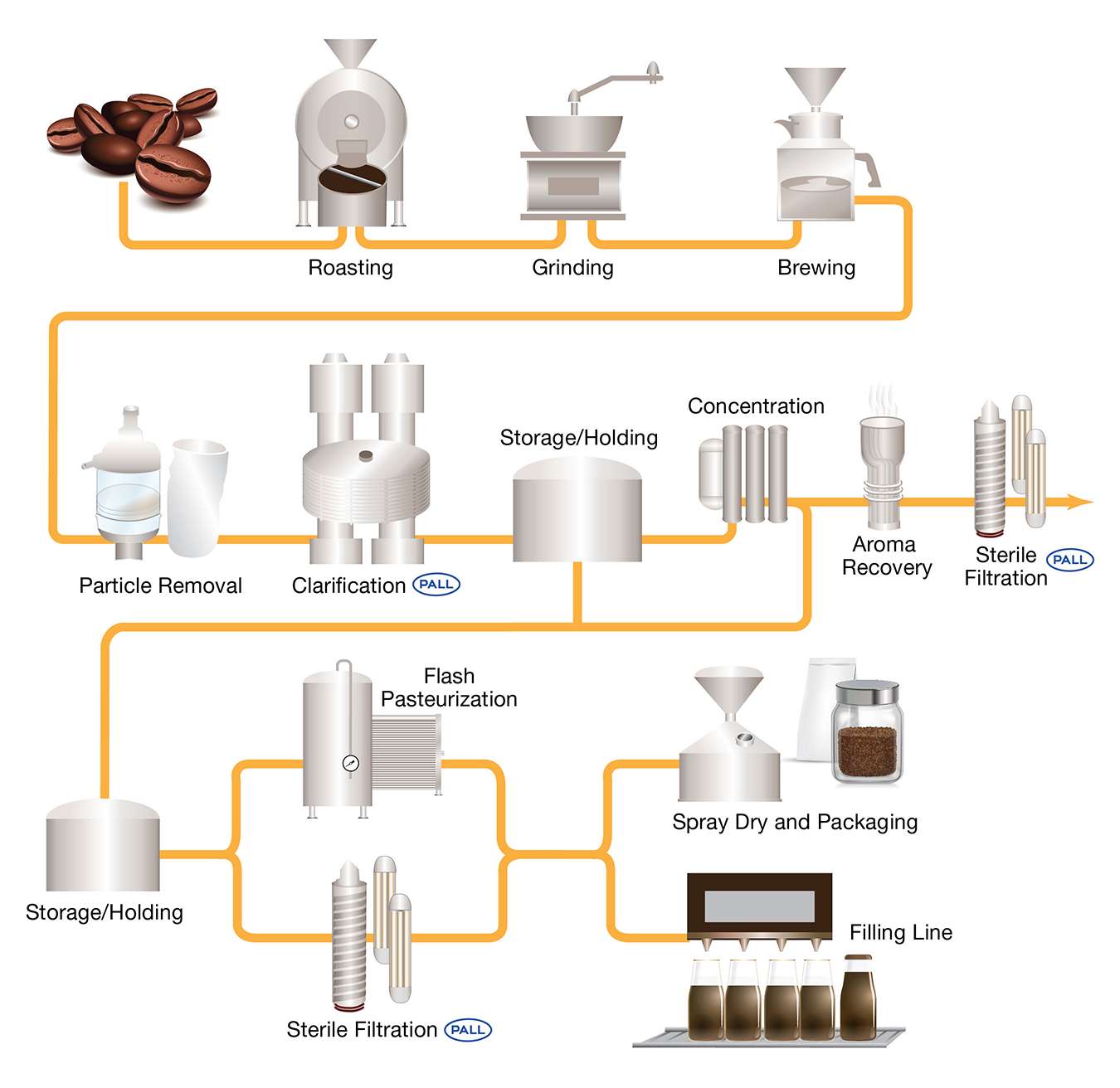
Additionally, guidance from the FDA is now recommending that firms subject to the pathogen reduction provisions of the juice HACCP regulation incorporate validated control measures for all C. botulinum spores into their HACCP plans that will be applied in the processing facility, and that will ensure that C. botulinum growth and toxin production will not occur should the juice be kept unrefrigerated in the distribution or by consumers. To maintain quality and control risk for C. botulinum contamination, a typical process train for cold brew coffee processing may look like the diagram shown below. Upstream processing for cold brew filtration typically includes particle filtration to remove coffee grinds and haze while downstream processing is designed for microorganism removal with technologies like pasteurization and membrane filtration.
Process Diagram Of Cold Brew Coffee Filtration
Click below to find out more about our solutions for cold brew coffee filtration.
We can help you find the right cold brew filtration solution for your needs. Contact us for a free 30 minute filtration consultation.