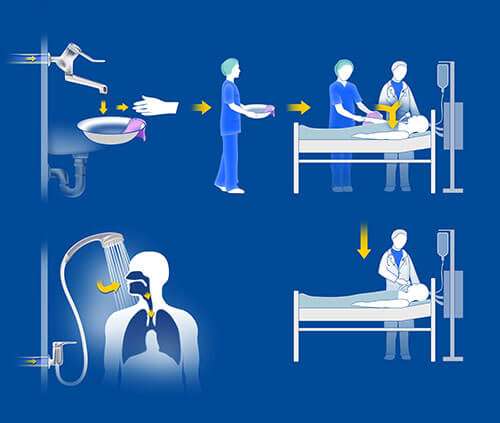
Inhalation and aspiration represent transmission pathways for Legionella spp.1, whereas Pseudomonas spp. is mainly transmitted by contact and aspiration.2,3 During daily routines, tap water is used for personal hygiene. For example, in the healthcare environment, due to the severity of their disease states, ICU patients often have multiple access devices such as catheters, drains and tracheal tubes. These portals represent potential entrance sites for bacteria from numerous sources. Droplets of contaminated tap water can inadvertently come into contact with those entrance sites.
Reference:
1. Hines et al., “Assessment of relative potential for Legionella species or surrogates enhances exposure from common water sources”, Water Res, 56: 203-13, 2014
2. Loveday et al., “Association between healthcare water systems and Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections: a rapid systematic review”, J Hosp Infect, 86(1): 7-15, 2014
3. Rogues et al., “Contribution of tap water to patient colonisation with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a medical intensive care unit”, J Hosp Infect, 67: 72-8, 2007
Tap Water Constitutes Risk of HAI

Fill Out The Form Below To Download Hospital Water Handout
Thank you for filling out the form! Please check your email to download the Hospital Water Handout.
What is biofilm and how does it develop?
In water distribution systems biofilm can develop within a few days even if the water meets drinking water criteria⁴. Biofilm can host bacteria, amoeba, algae and other microorganisms. Under low flow conditions, such as in dead legs, particularly thick biofilms can form.
Under the force of water flow biofilm shears off and biofilm particles can colonize other parts of the water distribution system⁵. External stress in the pipework, such as disinfection measures, can result in an increased expression of the biofilm phenotype cell which is responsible for the strong attachment of cells to a surface⁶.

Reference:
4. Exner et al., “Prevention and control of health care-associated waterborne infections in health care facilities”, Am J Infect Control, 33: S26-S40, 2005
5. Lindsay & von Holy, “Bacterial biofilm within the clinical setting: What healthcare professionals should know”, J Hosp Infect, 64: 313-25, 2006
6. Flemming & Wingender, “The biofilm matrix”, Nat Rev Microbiol, 8: 623-33, 2010

Fill Out The Form Below To Download Biofilm Summary
Thank you for filling out the form! Please check your email to download the Biofilm Summary.
Facts and Control Measures
Common source of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a Gram-negative bacillus which:
- is tolerant of a wide variety of physical conditions,
- has minimal nutrition requirements, and
- is a major opportunistic pathogen7,8.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa appears sporadically in drinking water distribution systems but seems to occur at a higher frequency in premise plumbing systems compared to water mains9,10.

References:
7. Asghari et al., “Rapid monitoring of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in hospital water systems: a key priority in prevention of nosocomial infection”, FEMS Microbiol Let, 343: 77-81, 2013.
8. Falkinham et al., “Epidemiology and ecology of opportunistic premise plumbing pathogens: Legionella pneumophila, Mycobacterium avium and Pseudomonas aeruginosa”, Environ Health Perspect, 123(8): 749-58, 2015
9. Moritz et al. “Integration of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Legionella pneumophila in drinking water biofilms grown on domestic plumbing materials”, Int J Hyg Environ Health, 213(3): 190-7, 2010
10. Wingender et al., “Mikrobiologisch-hygienische Aspekte des Vorkommens von Pseudomonas aeruginosa im Trinkwasser”. Energie Wasser-Praxis, 60(3): 60-6, 2009

Fill Out The Form Below To Download Pseudomonas Handout