Fueling a more circular economy
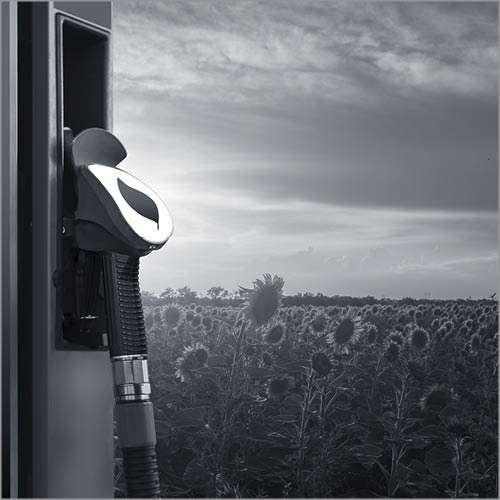
Advanced biofuels are made by processing oleochemical feedstocks like used cooking oils, tallow, and other waste and residue lipids. This solutions provides a safe, proven, and scalable way to decarbonize the transport sector, especially long-distance trucking and aviation. Advanced biofuels can reduce emissions by 70% to 80% compared to fossil fuels.
Advanced biofuels are also considered more sustainable than traditional (first generation) biofuels. Both chemically and functionally, traditional biofuels differ from petroleum-derived fuels and, therefore, can only be used in relatively low blends in existing vehicle engines. Consequently, advanced biofuels can be processed and distributed under existing petroleum infrastructure because they are functionally equivalent to petroleum fuels. Traditional biofuels predominantly use “food-based” feedstocks and are widely criticized for diverting edible crops to fuel production instead of food provision. Using waste bio-feedstocks that would otherwise go to landfills and serve no other purpose, advanced biofuels contribute to a circular economy. In addition, the use of existing refineries to produce renewable hydrocarbon fuels from these bio-feedstocks can reduce carbon emissions without overinvesting in refinery assets.
Advanced Biofuels are also known as:
- Hydroprocessed Esters and Fatty Acids (HEFA)
- Green diesel / Renewable diesel / hydrogenation derived renewable diesel (HDRD)
- Sustainable aviation fuels / Hydrotreated Renewable Jet fuel (HRJ) / synthetic paraffinic kerosene (HEFA-SPK)
- Hydrotreated Renewable Oils (HRO)
- Hydrotreated Vegetable Oils (HVO) / Hydrotreated Renewable Vegetable oils (HRV)
Already know the importance of Advanced Biofuels? Find out why the correct filtration is critical to equipment protection and final product quality.
Thank you for your inquiry